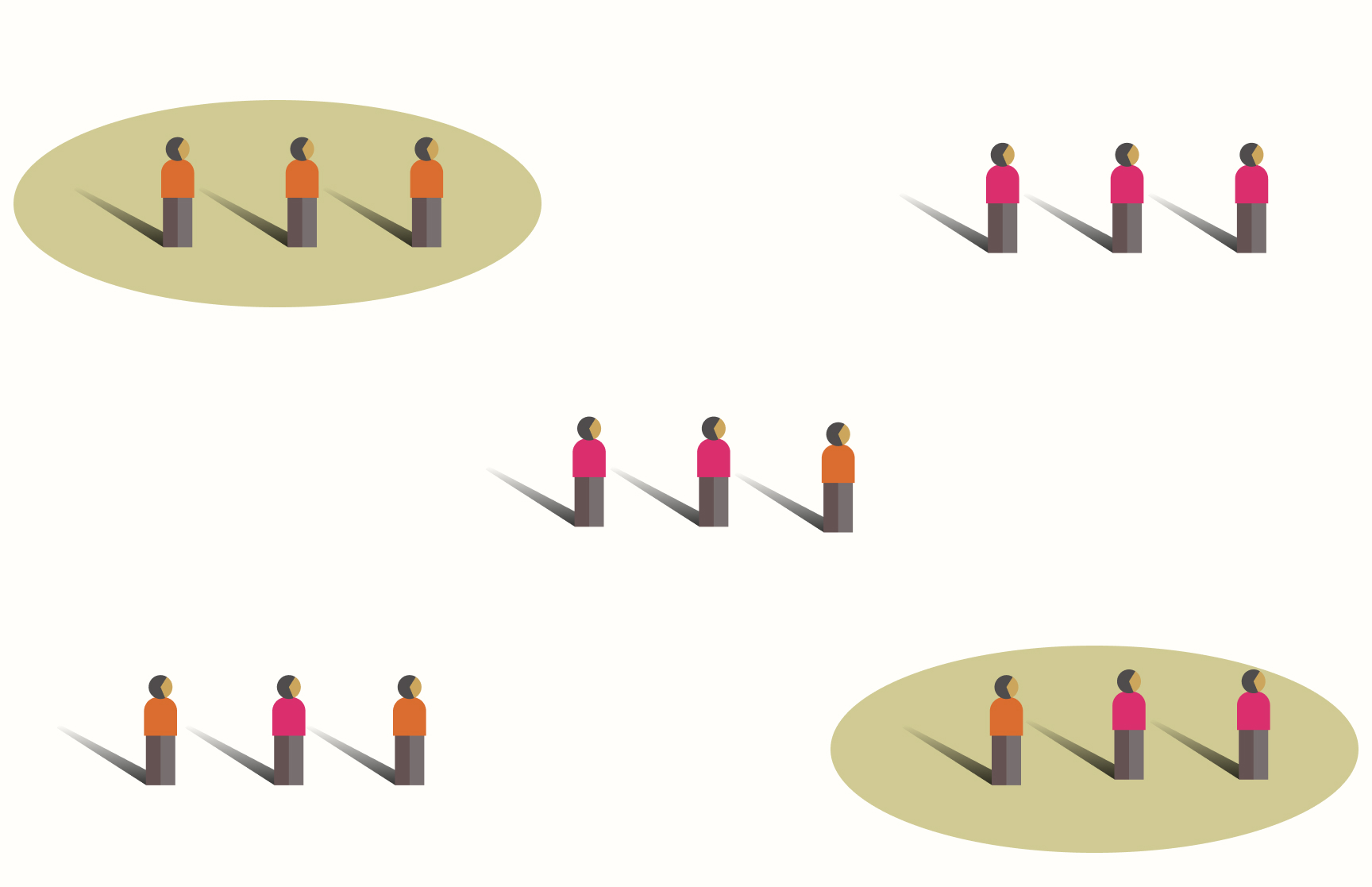
Cluster Sampling: What is it & How it Works?
Cluster sampling is a standard tool used in survey research. It’s a way to collect data from a group of people that is representative of the population as a whole. By taking this approach, you can minimize the risk of data bias and make sure that your results are accurate and reliable.
After reading this, you’ll better understand this sampling method and can make an informed decision about which method is best for your research needs. So, stay tuned and let’s get started with cluster sampling definition!
What is a Cluster Sampling?
Cluster sampling is a method of randomly selecting groups or clusters from a population to take observations from, usually in the form of randomized cluster samples. It can generate probabilities and statistics for a given sample or set of samples. This sampling method is often used when it is difficult or impossible to determine all population members.
Types of Cluster Sampling
There are three types of cluster sampling: one-stage sampling, two-stage sampling, and multistage sampling. Let’s take a look at each of them in detail!
1. One-Stage Sampling
Single-stage sampling is another name for one-stage sampling. When using this approach, sampling is done only once, and when the audience is not large enough.
For example, suppose you want to examine the grade point average of high school students in a specific state. It would undoubtedly be tough to poll every high school student in the state. So, you want to choose cities at random inside the state (clusters) to construct a random cluster sample within these clusters.
2. Two-Stage Sampling
Double-stage sampling is another name for two-stage sampling. This approach expands on the single-stage method to decrease the quantity of sampling required.
Using the same example as before, instead of surveying every student in each cluster, you will choose elements from each of the selected clusters. The units of the narrowed-down sample group will be the selected respondents for the research on high school students’ grade point average.
3. Multistage Sampling
Multistage sampling, like two-stage sampling, extends the process of getting the desired sample group by adding a few additional phases. This division is frequently required when time and money are exceedingly limited. You may keep breaking up the cluster to get progressively smaller random samples.
So, using the same example, you might divide the city clusters into school clusters and choose kids (units) randomly from each school until you achieve your required sample size.
Try the different cluster sampling types in a survey NOW!
What are the advantages of cluster sampling?
Probability sampling is a method that aims to collect data representative of a population. Cluster sampling is one of the most efficient methods because it allows you to sample large populations with reduced bias.
Plus, it yields more accurate results than traditional sampling methods. If you’re looking for a more efficient way to collect data, this should be your go-to method. So, what are you waiting for? Get started!
1. High reliability
This is a method that is reliable and can be used in a variety of different situations. It has the advantage of reducing bias and error, making it one of the most applicable methods for data collection.
2. Easy to implement
It is simple to implement and costs less than other sampling techniques. Plus, it’s random, so it doesn’t introduce any bias into the sample population.
3. Very efficient
It is very efficient because it eliminates the need for a random sample, which means that more representative data can be collected from a population with greater accuracy.
Make use of these advantages in a survey absolutely FREE
What are the disadvantages of cluster sampling?
This sampling method is very popular for sampling data. It’s simple to use and is often used to select a sample for research. However, it has its own set of disadvantages.
1. High Sampling Error
It is a method of data collection where a small number of items are sampled from a population. This method has the potential to generate high sampling errors.
2. Imprecise results with improper clusters
It can lead to inaccurate and imprecise estimates of population parameters. This is because it’s challenging to determine which clusters represent the population as a whole. Some researchers have even found that cluster samples can produce estimates much higher than those obtained from simple random sampling (SRS).
3. Least Representative
This strategy is the least representative of the population among all probability sampling techniques. Individuals inside a cluster have a propensity to have similar features. Therefore, with a cluster sample, there is a potential that the researcher will have an overrepresented or underrepresented cluster, which will skew the study’s conclusions.
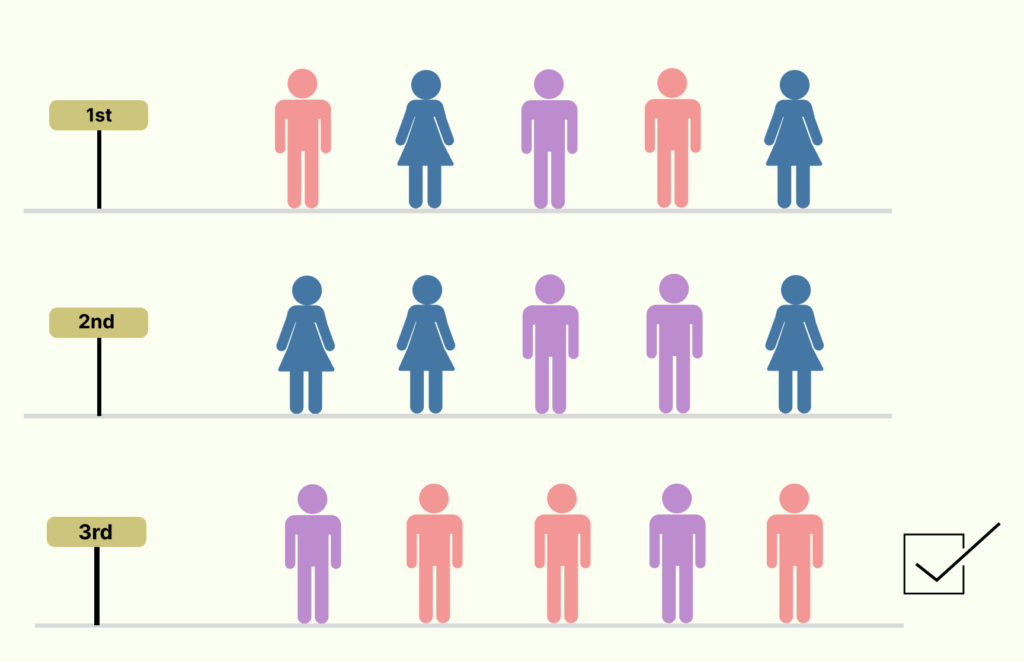
Cluster Sampling Examples
Assume you wish to assess the pay of airport workers in the United States. Because the United States has around 5,200 airports, the choice is made to define all 5,200 airports as clusters, with each airport’s personnel representing a cluster.
Using a simple random sampling approach, you may then choose 100 airports from your 5,200 clusters. The earnings of those 100 airport employees will serve as the critical data for your study.
You have eventually saved yourself the time to examine employees’ pay from all 5,200 airports. Traveling to all 5,200 airports will likewise cost less than the selected 100.
Create a survey and see it for yourself!
Cluster Sampling vs. Stratified Sampling
- In stratified sampling, a sample characteristic divides the population into homogeneous groups called strata. Then, individuals from each stratum are chosen, and the number of samples collected from each is proportional to the stratum’s presence in the population.
- Cluster sampling divides the population into clusters, primarily based on location, and then a cluster is chosen randomly.
- A cluster is chosen randomly in cluster sampling, whereas members are chosen randomly in stratified sampling.
- Stratified sampling has homogeneous individuals in each group (strata), whereas cluster sampling has diverse individuals in each cluster.
- Stratified sampling is slower, but cluster sampling is quicker.
- Stratified samples produce more accurate estimates because they account for the existence of each group within the population.
- Cluster sampling has a more significant rate of error by definition.
Why use Fynzo Survey Creator for cluster sampling?
The Fynzo online survey creator makes it easy to gather data from a cluster sample. This is useful for market research or customer segmentation, as you can easily collect feedback from an entire group of customers at once.
Additionally, the format ensures that all respondents have the same level of privacy so that their responses aren’t influenced by personal biases.
The Fynzo survey creator provides valuable insights into your target audience’s preferences and behavior, which can help you develop better products or services. By using this tool, you will be able to make informed decisions that will benefit your business in the long run.
Create a free survey and use cluster sampling method!
Conclusion
Cluster sampling is a method of sampling in which a sample is selected from a population by grouping units of the population with similar characteristics. This method is often used in research because it is efficient and allows for the collection of data from many individuals.
In this blog, we have explained cluster sampling in detail and provided an example to help you understand the method better. Make sure to read the blog to understand all the details, and then take the time to practice this sampling method on your next research project!
FAQs
1. Is cluster sampling biased?
Yes, this sampling method is biased because it relies on the idea that individuals in a small group are more similar to each other than they are to individuals in a larger group.
2. What is the difference between simple random sampling and cluster sampling?
Simple random sampling is the most common type of survey design, in which a list of respondents is selected at random from a population. Cluster sampling, on the other hand, is used when you want to sample particular groups within a population.







